Tesla Supercharger Network Expansion: The Complete 2025 Guide
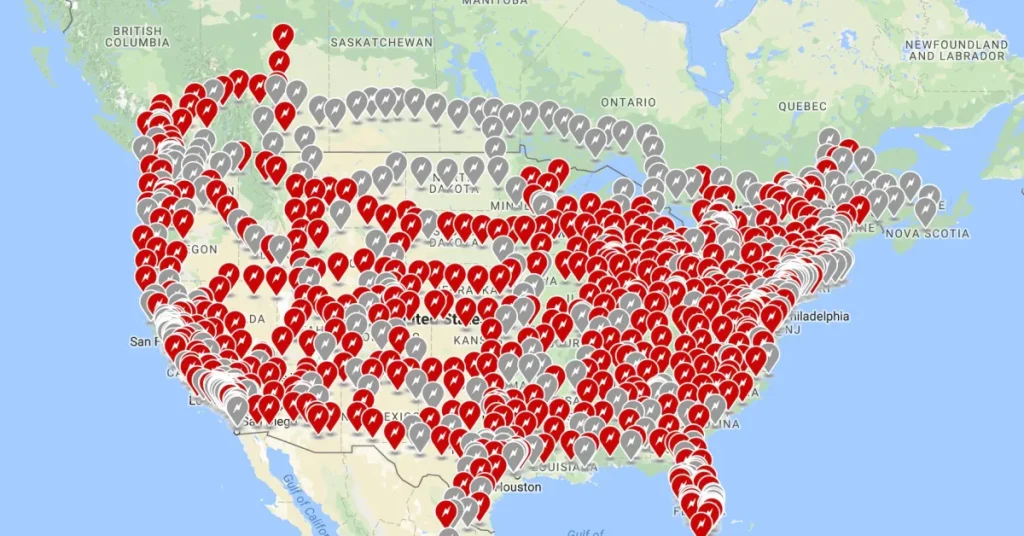
Table of Contents
The Growing Power of Tesla’s Supercharger Network
Tesla’s Supercharger network Expansion has been a cornerstone of the company’s strategy to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. As we look at the current EV landscape in mid-2025, one question continues to dominate discussions: Is the Supercharger network growing? The answer is a resounding yes, with Tesla’s charging infrastructure expanding at an unprecedented pace across the globe.
This comprehensive guide explores Tesla’s Supercharger expansion, its impact on electric vehicle adoption, and addresses key questions about this revolutionary charging system that continues to reshape how we think about transportation infrastructure.
What is a Supercharger Network? Understanding the Basics
Before diving into expansion details, let’s clarify: What is a Supercharger network? Tesla’s Supercharger network is a proprietary system of fast-charging stations designed specifically for Tesla electric vehicles. Unlike standard charging options, Superchargers deliver direct current (DC) power directly to the battery, bypassing the vehicle’s onboard charger.
Key features that define the Supercharger network include:
- Fast charging capability: V4 Superchargers can add up to 250 miles of range in just 15 minutes
- Strategic placement: Located along major travel routes and in urban centers
- Seamless integration: Automatic billing through Tesla accounts
- Real-time availability: Instant status updates through the Tesla app
- Expanding accessibility: Now opening to non-Tesla vehicles in many regions
With over 50,000 Superchargers operational worldwide as of May 2025, the network has evolved from a Tesla-exclusive amenity to a critical piece of global EV infrastructure.
Supercharger Network Expansion: By the Numbers
The pace of Tesla’s Supercharger deployment has accelerated dramatically over the past 18 months. Current statistics show:
- Year-over-year growth: 35% increase in total Supercharger stalls worldwide
- New markets: Expansion into 12 previously unserved countries
- Urban concentration: 40% increase in metropolitan area coverage
- V4 deployment: Over 15,000 next-generation Superchargers installed globally
- Non-Tesla access points: 75% of European stations and 45% of North American stations now open to other EVs
This rapid expansion represents Tesla’s largest-ever investment in charging infrastructure, with the company allocating over $3 billion to Supercharger deployment in 2024-2025 alone.
NACS Adoption: Which Cars Use NACS?
One of the most significant developments in EV charging has been the widespread adoption of Tesla’s North American Charging Standard (NACS). But which cars use NACS? As of mid-2025, the answer includes virtually every major automotive manufacturer selling vehicles in North America:
- Ford: All EVs produced after January 2025
- General Motors: Entire EV lineup starting with 2025 models
- Rivian: All vehicles through adapter program, native support in 2025 models
- Volkswagen Group: Adapters for current models, native in 2026 lineup
- Hyundai/Kia: Transition beginning Q3 2025
- Toyota: Announced NACS implementation for 2026 models
- BMW Group: Adapter program launched April 2025
- Mercedes-Benz: NACS-compatible vehicles starting production
- Nissan: Committed to NACS implementation by 2026
This industry-wide shift to NACS represents a remarkable pivot from competing standards toward Tesla’s connector design, effectively making the Supercharger network the default charging infrastructure for most new EVs in North America.

Strategic Network Deployment: Beyond Highway Corridors
Tesla’s expansion strategy has evolved beyond simply connecting major cities via highway corridors. The latest deployment focuses on:
Urban Supercharging
Tesla has dramatically increased urban Supercharger locations, targeting:
- Apartment and condominium complexes
- Shopping centers with extended hours
- Entertainment districts
- Municipal parking facilities
- Business parks and office complexes
Destination Charging Complementation
The Supercharger expansion now strategically complements Tesla’s destination charging program:
- Resort and vacation destinations
- National parks and scenic areas
- Cultural attractions and museums
- Sports venues and event centers
International Growth Focus
Particular emphasis has been placed on:
- Asia-Pacific expansion, especially Southeast Asia
- Eastern European coverage
- Middle East and North Africa deployment
- Latin American market development
The Leadership Question: Why Did Elon Fire the Supercharger Team?
Industry observers frequently ask: Why did Elon fire the Supercharger team? This refers to the early 2024 restructuring of Tesla’s charging infrastructure division. While some media reports characterized this as a mass firing, Tesla clarified that it represented a strategic realignment.
The reorganization had several key aspects:
- Leadership consolidation: Bringing charging infrastructure under vehicle engineering
- Process streamlining: Eliminating redundancies between teams
- Deployment acceleration: Creating a more nimble installation process
- Technology integration: Aligning charging and vehicle technology development
- Non-Tesla access program: Dedicating resources to expanding compatibility
This reorganization, while disruptive in the short term, appears to have accelerated deployment rates. Tesla reported a 23% increase in new Supercharger installations in the six months following the restructuring compared to the prior six-month period.
Technical Advancements: The V4 Supercharger Revolution
The V4 Supercharger rollout represents the most significant technological leap in Tesla’s charging infrastructure since the introduction of V3 chargers in 2019. Key improvements include:
- Higher peak power: Up to 350 kW charging capability
- Longer cables: Accommodating all vehicle designs and parking configurations
- Improved thermal management: Maintaining optimal charging speeds in extreme conditions
- Enhanced grid integration: Better load balancing and power management
- Solar and Megapack integration: Energy storage and generation at select locations
- Modernized user interface: Digital displays with charging information
- Non-Tesla compatibility: Built-in support for other EVs via adapters or native NACS
These technical advancements maintain Tesla’s leadership position in charging speed and reliability, even as competitors race to deploy their own fast-charging networks.
User Experience: The Supercharger Advantage
Tesla continues to differentiate its charging experience through software integration and station design:
Tesla App Integration
- Automatic navigation routing through Superchargers
- Real-time charger availability and wait times
- Automatic billing and payment processing
- Charging session monitoring and notifications
- Trip planning with projected charging stops
Station Amenities
- Weather protection and lighting
- Proximity to restrooms and food options
- Security cameras and monitoring
- Pull-through spaces for vehicles with trailers
- Increased stall count to reduce waiting times

Financial Aspects of Supercharger Expansion
Tesla’s expansion strategy contains several financial components that ensure long-term sustainability:
Revenue Streams
- Direct charging fees from Tesla owners
- Premium pricing for non-Tesla vehicles
- Commercial partnership arrangements
- Grid services and energy arbitrage
- Advertising potential through Supercharger displays
Investment Sources
- Internal Tesla capital allocation
- Government grants and incentives
- Utility partnerships and contributions
- Retail host cost-sharing arrangements
- Climate credit monetization
Return on Investment
- Enhanced vehicle sales through infrastructure advantage
- Customer loyalty and satisfaction metrics
- Competitive positioning against other manufacturers
- Energy market participation opportunities
- Real estate appreciation at owned locations
Challenges to Continued Expansion
Despite impressive growth, Tesla faces several challenges in continuing its Supercharger expansion:
Physical Constraints
- Grid capacity limitations in some regions
- Real estate costs and availability
- Construction permitting delays
- Electrical infrastructure upgrades
- Weather-related installation challenges
Competitive Landscape
- Increasing investment from alternative networks
- Government-sponsored charging initiatives
- Utility-owned charging infrastructure
- Oil company diversification into EV charging
- Commercial property charging deployments
User Experience Concerns
- Increasing wait times at popular locations
- Non-Tesla vehicle integration complexities
- Payment processing variations by region
- Maintenance and reliability challenges
- User education for new EV owners
Future Outlook: What’s Next for Tesla Superchargers
Looking ahead to late 2025 and beyond, Tesla’s Supercharger roadmap includes several exciting developments:
Technological Evolution
- Testing of higher-power 500+ kW charging for Semi and Cybertruck
- Further cable management and connector improvements
- Enhanced weatherproofing for extreme environments
- Wireless charging pilots at select locations
- Improved solar and battery storage integration
Deployment Strategy
- 100% increase in total Supercharger stalls by end of 2026
- Complete coverage of all major global highways in served markets
- Urban density doubling in top 50 metropolitan areas
- Rural access program for underserved communities
- Strategic placement near emerging EV tourism destinations

Conclusion: The Expanding Power of Supercharging
Tesla’s Supercharger network expansion represents far more than just additional charging points—it’s a fundamental reshaping of transportation infrastructure. By creating a reliable, convenient, and increasingly universal charging experience, Tesla continues to address the primary concern limiting EV adoption: charging anxiety.
The continued growth of the Supercharger network, combined with the industry-wide adoption of the NACS standard, demonstrates how Tesla’s influence extends far beyond its vehicle sales. As the network expands, it creates a virtuous cycle: more chargers lead to more EVs, which justifies more chargers, accelerating the transition to sustainable transportation.
Whether you drive a Tesla or one of the many other EVs now compatible with Superchargers, the expanding network brings us closer to a future where electric vehicles are the obvious and convenient choice for all drivers.
FAQs About Tesla Supercharger Network Expansion
How quickly is the Supercharger network growing?
Tesla is currently adding approximately 5,000 new Supercharger stalls per quarter globally, representing a 35% year-over-year growth rate.
Can non-Tesla vehicles use all Superchargers?
Currently, about 75% of European Superchargers and 45% of North American Superchargers are open to non-Tesla vehicles, with plans to expand access further by the end of 2025.
What is the cost difference for non-Tesla vehicles?
Non-Tesla vehicles typically pay 20-30% more per kWh than Tesla owners, though subscription options are available to reduce this premium.
How does Tesla decide where to build new Superchargers?
Tesla uses a combination of travel corridor analysis, existing owner density, anticipated sales growth, and strategic partnerships to determine new Supercharger locations.
Will Tesla continue to build Superchargers now that other networks exist?
Yes, Tesla has accelerated its Supercharger deployment despite the growth of alternative networks, viewing charging infrastructure as a key competitive advantage and revenue opportunity.
What happens to Superchargers during power outages?
Select Supercharger stations are being equipped with Megapack battery storage and solar generation to provide resilience during grid outages, with plans to expand this capability.
How does Tesla maintain Supercharger reliability?
Tesla employs remote monitoring, preventative maintenance schedules, and rapid response teams to ensure over 99.5% uptime across the Supercharger network.
Will Tesla ever license Supercharger technology to other operators?
While Tesla has opened its patents, it has not indicated plans to license Supercharger operation to third parties, preferring to maintain control over the user experience.
How does Tesla’s Supercharger network compare to competitors?
Tesla’s network remains significantly larger than any competitor in terms of total stalls, geographic coverage, reliability metrics, and charging speed capabilities.
What environmental measures does Tesla take with Superchargers?
New Supercharger installations increasingly include solar canopies, battery storage, water retention systems, and sustainable materials in construction.
For more info;Visit – TESLA EV
More Car Review: 2016 Volkswagen Golf GTI